Food pad dermatitis in broilers
Foot pad dermatitis (FPD or lesions) can be a severe problem in broiler houses, leading to reduced technical results and economic losses. It is caused by wet and sticky litter. As it is a multi-factorial problem, a multi factorial approach should be applied to both solve and prevent foot pad dermatitis. The causes for FPD differ between farms and therefore the actions needed to be taken against FPD also differ between farms.
Factors influencing foot pad dermatitis can be categorized in three groups. The first group consists of the animal factors which are directly related to the birds. These are for example factors like breed, gender, age, body weight and health status. The second group are factors influenced by management. Examples are ventilation, temperature inside and outside the house, bedding material, bird density and housing conditions like drinking system, water pressure, litter, light, micro climate, spread of birds and manure. The third group of factors influencing foot pad dermatitis is nutrition. Nutrition has a maximum influence on foot pad dermatitis of 30%. In this article will focus on some of the key aspects.
Raw materials
Many trials have been conducted to study the effect of raw materials on foot pad dermatitis. These studies show us we need to consider different factors within raw materials. For example, soy bean meal is mostly used as the main protein source with a high digestibility. However potassium also goes up with the use of soy bean meal which affects FPD negatively. Moreover the protein concentration in soy bean meal is influencing FPD indirectly. The lower the protein concentration, the higher the soluble Non Starch Polysaccharides fraction will be in soy bean meal, which also affects FPD in a negative way. Using other alternative protein sources can be a solution. When choosing other raw materials, it is important to consider parameters such as viscosity, indigestible crude protein and/or anti-nutritional factors, ideal digestible amino acid pattern in the resulting feed. All these factors negatively affect FPD.
Nutrients
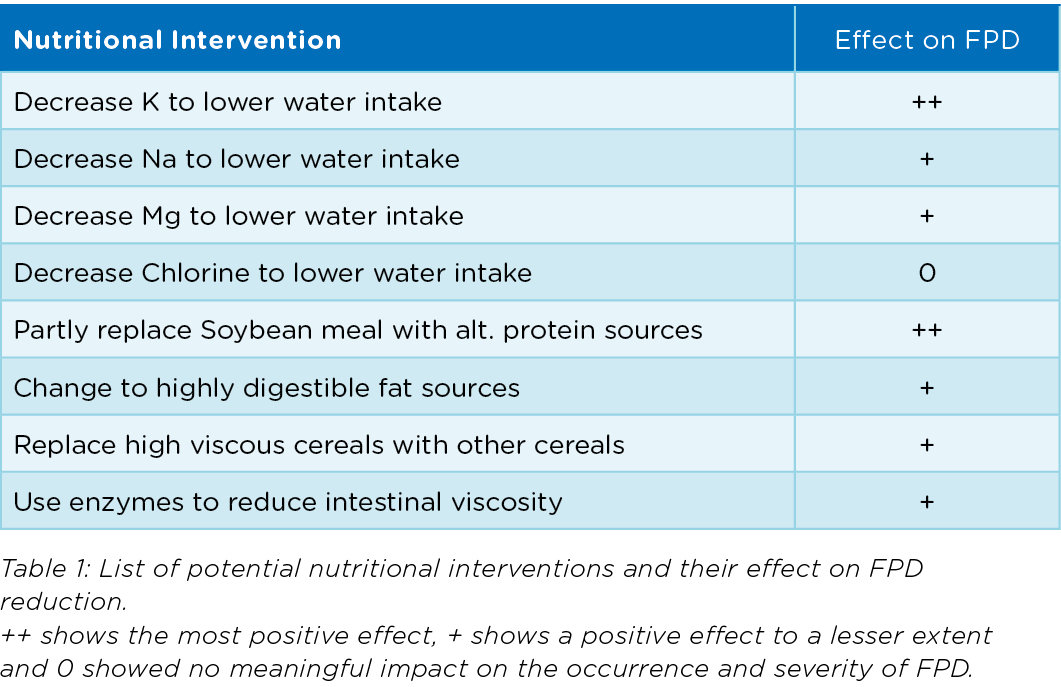
FPD is caused by wet and sticky litter so this need to be prevented. Minerals are important nutrients to keep water consumption under control. Too high mineral levels
(especially Mg, K, Na) lead to higher water intake, resulting in more water in the manure.
To prevent sticky litter, it is also important to maintain good gut health. When gut health is affected, digestion will become worse. Bacterial overgrowth is occurring, bile salts are deconjugated by bacteria, resulting in a decreased fat digestion. More fat in the excreta leads to more sticky litter from where water will not evaporate easily. Increased viscosity in the intestine is also leading to dysbacteriosis and therefore a higher moisture content in the excreta. Helping the birds by choosing the right combination of raw materials together with the right corresponding choice of enzymes will reduce viscosity and improve digestion (see Koudijs Newsletter Nov. 2020). In certain cases it is useful to add additives to the feed either improving gut health or improving the balance of the microbiota. We did a lot of research trials, resulting in possible adjustments in the feed that have proven their benefit in field conditions. Table 1 summarizes the effect of nutritional interventions that were studied during these trails. Many nutritional adjustments lead to a reduced performance or a strong increase in feed costs. Depending on the severity of the FPD problem we know how to reduce FPD significantly in the most economical way. By combining selected nutritional adjustments and best management practices we optimize the best solution for your situation. Please contact us when you would like to know more about the this topic.